
How automation in agriculture boosts productivity with smart irrigation
Automation in agriculture has emerged as a strategic solution to tackle global challenges related to productivity and sustainability. As the demand for high-quality food continues to rise, integrating innovative technologies for instrumentation and mechanization has become the key to meeting this need — balancing greater efficiency with cost-effectiveness and environmental responsibility.
This article delves into how automation is transforming the agricultural sector, highlighting technological innovations developed by Altus, the economic and environmental benefits achieved, the challenges that still need to be addressed, and the prospects for the agri-food industry.
The main challenges of the agribusiness sector and the solution through automation
The agribusiness sector faces complex and growing challenges: the need to produce more with less while adopting environmentally responsible practices and striving for greater efficiency in resource use, such as water, energy, and fertilizers, to meet the increasing global demand. In this context, automation emerges as a strategic solution to overcome these challenges, enabling precise control of agricultural processes and promoting the smart use of inputs.
Through the integration of advanced systems and technologies, automation allows for real-time monitoring, adjustment, and optimization of operations, ensuring that each stage of production is carried out more effectively and cost-efficiently. Both small-scale farmers and large agribusinesses benefit from these innovations. Small producers can improve resource management and minimize waste, while large companies can implement large-scale automated solutions, boosting productivity and supply chain traceability. This progress also supports the adoption of regenerative agricultural practices, fostering better soil health, water conservation, and reduced greenhouse gas emissions.
The role of the Nexto Xpress Series in water pumping and distribution solutions
Automation applied to irrigation projects is a clear example of how this technology is helping the agricultural sector meet the growing demands of the field. Among the most notable solutions, Altus’ Nexto Xpress controllers stand out, offering a combination of efficiency, versatility, and robustness. Their application in irrigation systems illustrates how automation can transform traditional practices and deliver significant benefits, such as:
- Optimized Pump Control: Nexto Xpress controllers enable precise management of frequency inverters, which regulate electric motors used in water pumping. This ensures pumps operate efficiently, reducing energy consumption and optimizing water flow according to the specific needs of each irrigated area.
- Connectivity and remote monitoring: With communication technology via MQTT (Message Queuing Telemetry Transport), a lightweight and highly efficient protocol that enables data exchange between devices like sensors and IoT equipment, remote monitoring and real-time data analysis are possible, even in hard-to-reach locations.
- Speed and flexibility: Designed to meet the needs of machines and small processes, Nexto Xpress controllers offer a complete solution that combines performance with advanced connectivity. Their diverse communication interface options and support for major protocols make the series an ideal choice for those looking to modernize their operations with excellent cost-effectiveness.
Altus’ success cases in South Africa and Turkey highlight the efficiency of the Nexto Xpress Series in managing processes with agility and simplicity, providing a lightweight and versatile solution for various applications.
In Turkey, the application combined integration with weather forecasts and automated decision-making capabilities in the pumping system. Using the MQTT protocol, the Xpress controller reads data on a local workstation equipped with Node-RED, collecting detailed information on weather conditions for the next 72 hours, such as wind, temperature, humidity, and rainfall probability.
Based on this analysis, the system automatically adjusts water flow and the number of pumps in operation, ensuring optimal irrigation levels are maintained. This process not only reduces average pipe pressures, minimizing damage rates, but also significantly cuts energy and water consumption. The controller’s direct communication with a cloud-based supervisory system ensures efficient remote monitoring, enabling real-time system tracking. This allows for rapid identification of faults or operational issues, facilitating swift intervention by technical teams and enhancing system availability and reliability during operation.
In South Africa, the Nexto Xpress controllers also communicate remotely with a cloud supervisory system using the MQTT protocol. This protocol is ideal for applications requiring maximum efficiency in data transmission, even in environments with limited infrastructure. Its low overhead makes MQTT particularly advantageous for remote locations, enabling monitoring and data exchange while optimizing the available transmission capacity.
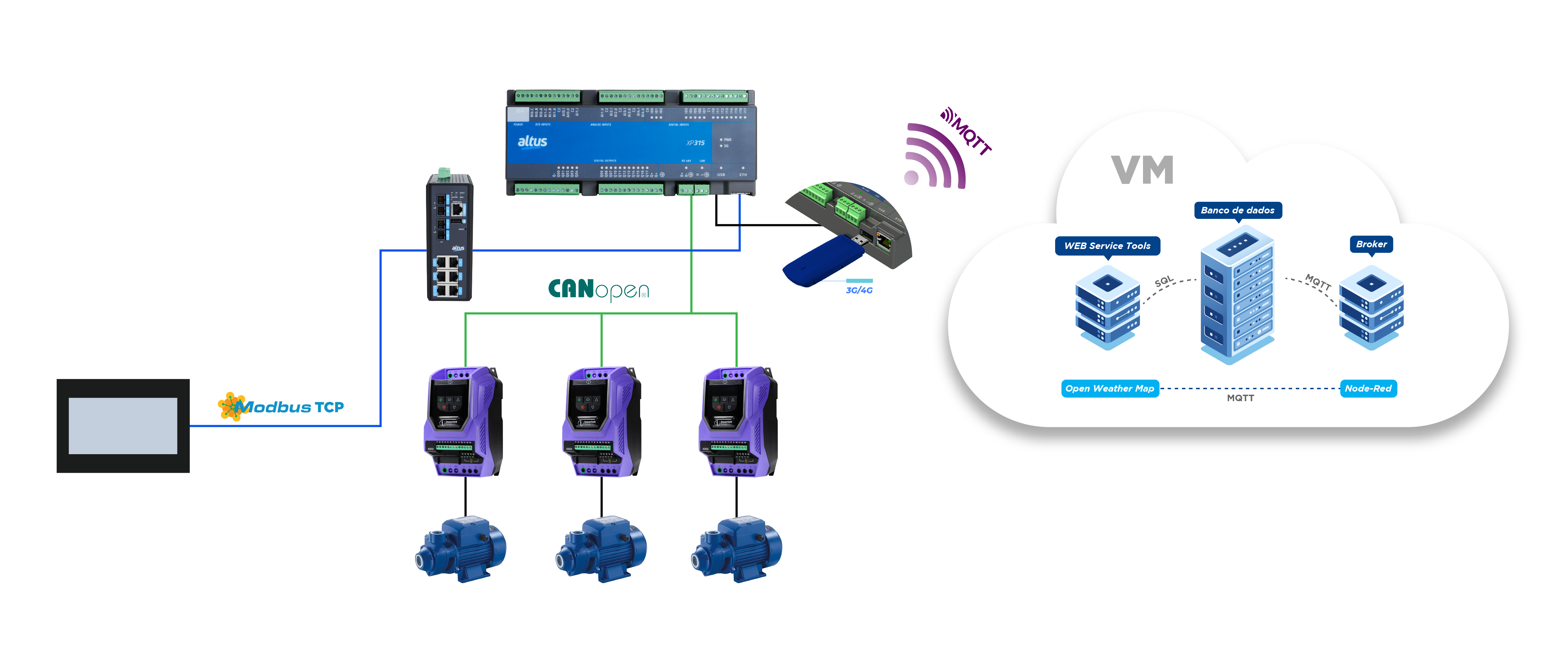
Highlights of this solution’s architecture:
Nexto Xpress XP315 + X2 Base 5" HMI
- MQTT for cloud integration.
- Node-RED integration with dashboards.
- Weather forecasts via "Open Weather Map".
- Pump control with PID pressure regulation.
- Functional blocks (FB) for water applications.
- Smart engineering for CANopen.
Results:
- No pressure shocks in pipes due to rapid pressure control.
- Irrigation planning up to three days in advance.
- Approximately 35% reduction in water consumption thanks to more accurate forecasting.
- 20% reduction in energy consumption through the use of inverters and weather forecasts.
The optimization of these processes enables intensive farming in smaller areas, reducing environmental impacts while increasing productivity and improving food quality. With precise control of ideal conditions for plant growth, agricultural automation minimizes resource waste and establishes itself as a key practice to address global challenges related to crop security and smart resource management.
Overcoming the challenges of implementing automation technologies to optimize crops
Despite its numerous benefits, the large-scale implementation of automation in the agricultural sector still faces significant challenges that must be addressed to ensure effective adoption. Key obstacles include:
- Seasonality of operations: The cyclical nature of agriculture requires that the installation and integration of automated systems be carried out without disrupting ongoing crops or halting the production flow. This demands careful planning and more flexible solutions that can adapt to the different phases of the agricultural cycle, from planting to harvest. Technologies must also be robust enough to handle climatic variations and the specific demands of each crop.
- Communication infrastructure: Many rural areas still lack adequate infrastructure, such as high-speed internet, 5G connectivity, or reliable communication networks. This limitation directly impacts the efficiency of connected technologies like IoT sensors, remote monitoring systems, and artificial intelligence. Investments in digital infrastructure are essential to expand connectivity and unlock the full potential of automation in agriculture.
- Implementation costs: The initial cost of acquiring and installing automated equipment is another significant challenge. While the long-term benefits are clear, many farmers, particularly small and medium-sized ones, may struggle to finance these innovations.
- Training and adaptation: Introducing automated systems requires that farmers and operators be adequately trained to use them. A lack of proper training can delay or limit the effectiveness of automation. Therefore, creating technical training programs and providing ongoing support is essential to maximize results.
Even so, continuous technological advancements and declining equipment costs are making automation more accessible, even in areas with limited infrastructure. Compact and affordable systems, like our Nexto Xpress Series, stand out as examples of overcoming these obstacles. Designed to deliver all-in-one solutions, they operate efficiently even with limited resources, offering intelligent and secure tools for process monitoring and control.
Moreover, government programs and private initiatives in Brazil have been investing in expanding connectivity in rural areas, recognizing that digital infrastructure is key to driving the modernization of the agricultural sector. Strategic partnerships with technology companies and internet providers are enabling the development of more advanced systems tailored to the specific needs of agribusiness. These efforts ensure that even the most remote regions can reap the benefits of automation and digitalization.
Automation and agriculture 4.0: key trends shaping the future
The future of automation in the agribusiness sector presents a promising outlook, driven by the growing global demand for food and the adoption of advanced technologies to optimize every stage of the production chain—from how food is produced to how it is distributed and managed. Among the key trends shaping this future are:
- Autonomous systems: Autonomous machines and equipment, which operate with minimal human intervention, are delivering greater precision and consistency in production processes, reducing waste and operational costs. Autonomous tractors, harvesters, and drones, for example, are already being used for planting, irrigation, and crop monitoring, enabling producers to focus on strategic decision-making.
- Controlled cultivation: Technologies such as vertical farming, automated greenhouses, and hydroponic systems are redefining the boundaries of agricultural production. These methods allow for strict control over factors like temperature, humidity, light, and nutrients, resulting in higher yields and superior quality crops—even in urban areas or regions with challenging climatic conditions.
- Technological integration: The combination of technologies like the Internet of Things (IoT), Artificial Intelligence (AI), Big Data, and weather forecasting is empowering farmers and agribusinesses to make more informed decisions. IoT sensors enable real-time monitoring of soil, plants, and equipment, while data analysis software and AI process this information to deliver valuable insights.
Automation reduces reliance on intensive labor, enhances business security, and opens new possibilities for production in regions previously considered unviable. This advancement democratizes access to more sophisticated equipment, enabling small and medium-sized producers to keep up with global trends and improve their competitiveness in the market.
The emerging landscape is one of an increasingly connected and optimized agribusiness sectors, ready to tackle the challenges ahead. Companies like Altus are leading this transformation, demonstrating that innovation through the automation of operations is essential for greater efficiency and profitability. By offering customized and accessible solutions, we are helping farmers and industries adapt to the demands of an ever-evolving market.




