The versatility of the IoT gateway
Increasingly present in our lives, technology offers a series of smart and customizable devices that promise to make our daily lives easier. The concept of IoT, which stands for Internet of Things, proposes connecting everyday objects, such as light bulbs, watches and cars, to a network, facilitating our routine and contributing to the evolution of devices, which become more interactive and intelligent.
The gateway, equipment which we`ve already talked about here on the I&A Blog, is one of those devices. With it, it is possible to make the connection between equipment located in different networks and that communicate through different standards. In this article, we are going to delve into this concept and talk about the application of gateways in the IoT environment and how their use can benefit the industry!
What is an IoT gateway?
The IoT gateway works as a connection point between several technologies, allowing equipment that use different communication standards to converse and exchange data with each other. That means it serves as an input and output point for all information on the network, facilitating the exchange of information by adapting physical media and communication protocols.
The IoT gateway is also a smart device that can be used in Edge Computing applications, routing data exchange between equipment and the PLC responsible for the process, instead of storing them in a database or in the cloud. This prevents information overload outside the devices and communication delays. In this way, the device filters unnecessary or routine information that prevents the equipment from working and transmits only unusual or critical data, avoiding system overload.
Another positive point of using IoT gateways is the reduction in infrastructure costs. As the most advanced sensors on the market are capable of generating and processing tens of thousands of data per second, they do not require the use of a PLC to process this information before storing it. However, it is necessary to use some resources to bring the data from the sensors to the supervision system. In this case, IoT gateways can be used to send the information collected by the sensors directly to the local database or to the cloud, reducing infrastructure expenses and increasing process efficiency.
How to use an IoT gateway in your factory
As they are fully connected to the Internet of Things concept, IoT gateways have a wide range of uses. One such application is in building communication networks with intelligent offices. In building applications like these, it is common to have hundreds of sensors for measuring variables such as temperature, lighting, energy efficiency, air quality and security system signals, which ends up generating a large volume of data. Here, the gateway`s job is to transmit this data to the PLC. In the case of the temperature variable, it sends data to the control device informing if it is colder or hotter than the predetermined in the system. If the temperature is too high, the PLC can adjust the air conditioning setting and cool the room.
High connectivity devices such as IoT gateways are easily applicable in architectures that use Altus products. As an example, let`s imagine a factory with different processes interconnected through a MODBUS RTU network and controlled by DUO Series PLCs. To increase the level of control and qualify of the decision-making process, if the management team decides to upgrade the plant by installing a supervision system with interactive dashboards. In order for shop floor information to be presented by the new system, it is necessary to collect data directly from the PLCs.
However, there is a problem: the DUO family devices communicate only through the protocol used in the control network, the MODBUS RTU, and also do not have Ethernet-type interfaces, only RS-485 and RS-232 serial ports. In this case, so that the new supervision system could be installed without major changes in the control architecture, an IoT gateway could be used as a translator between the PLC and the supervisory system. The equipment could receive data from the controller in MODBUS RTU, through one of the serial interfaces, and convert it to a language compatible with the supervisory, such as the OPC UA protocol.
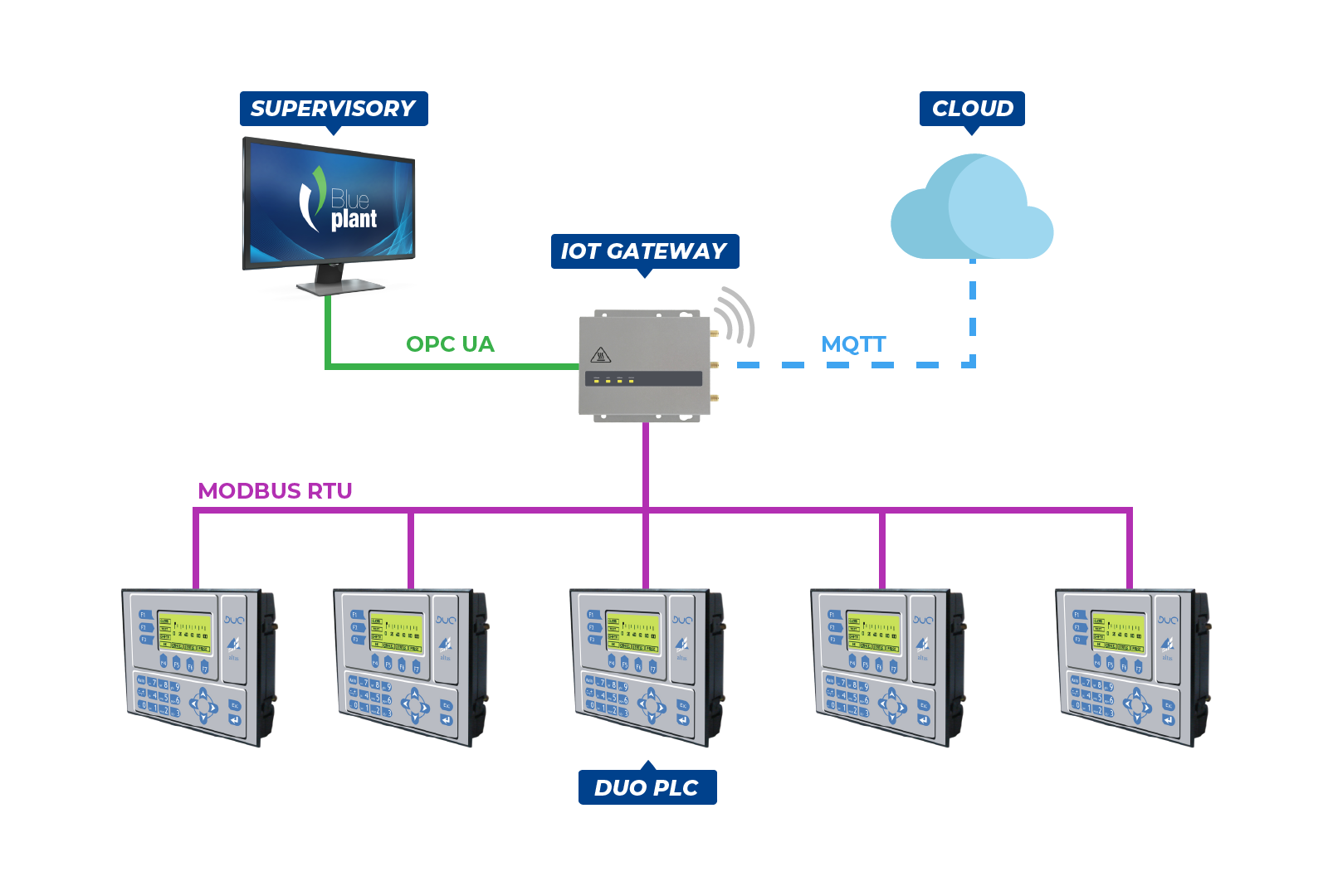
Another option would be to write the collected information into a database hosted in the cloud. In this case, the gateway could convert MODBUS RTU data to MQTT standard, one of the most used communication protocols in IoT applications today. This same example is valid for different network architectures that use any PLC or equipment, from Altus or third parties, with support for a protocol and demand conversion to a different standard.
Nexto Xpress PLC as an IoT Gateway
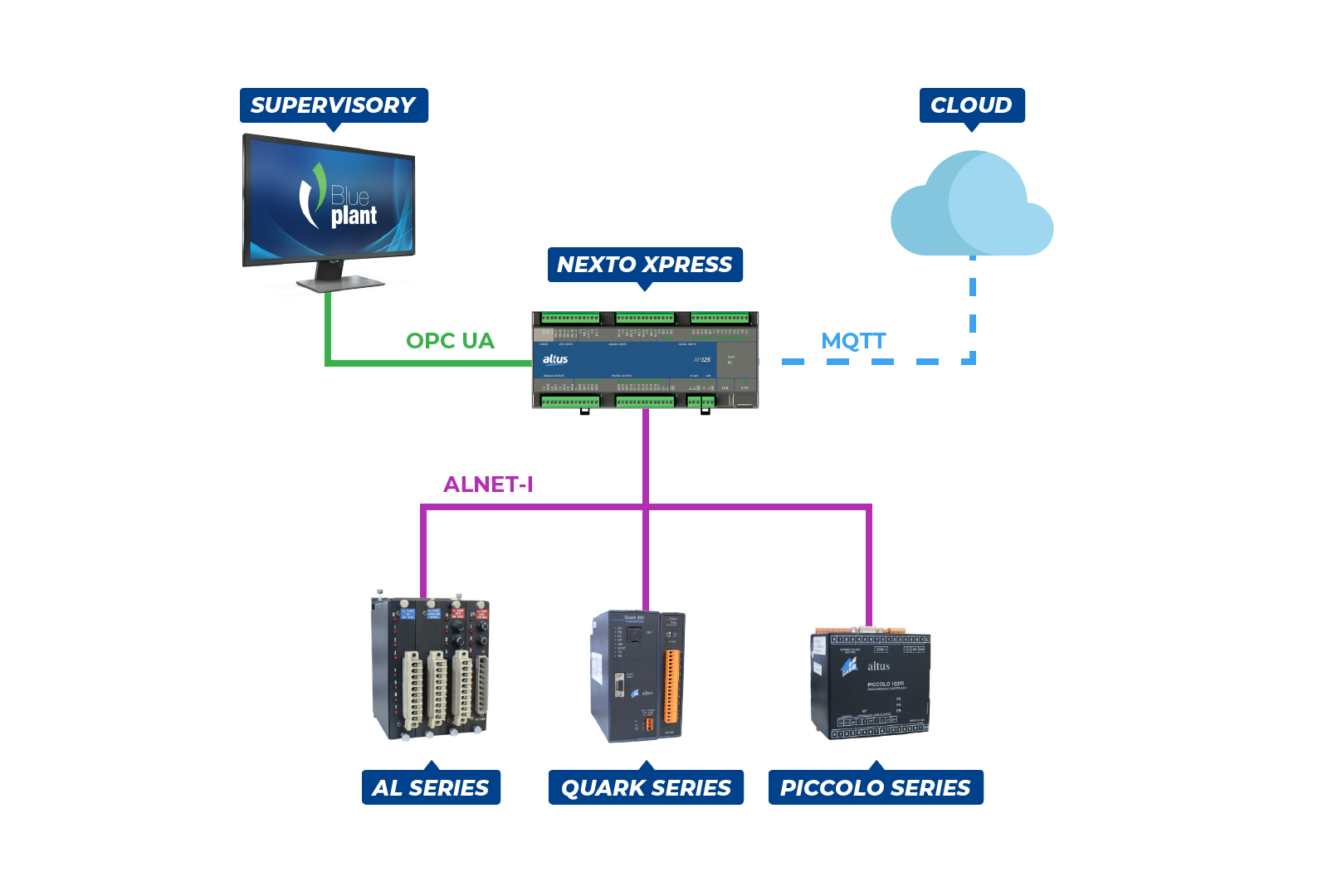
For applications that demand higher processing power and gateway connectivity level, a programmable controller can be applied as a translation and connection device between different machines and systems. However, for this, the equipment in question must have advanced technology and support different communication protocols, such as the case of Nexto Xpress, IoT Ready PLC manufactured by Altus.
One example we can mention is the use of the PLC as an IoT gateway for communication between older Altus product families, such as the AL series, Quark and Piccolo, and new IoT devices. In this case, Xpress can translate the data sent by the equipment, which use the ALNET I standard, to EtherNet/IP or a more common protocol today. As in the previous example, the Nexto Xpress PLC could also transmit this data to a supervisory, using the OPC UA or MODBUS TCP protocols, and to a cloud database, using MQTT.
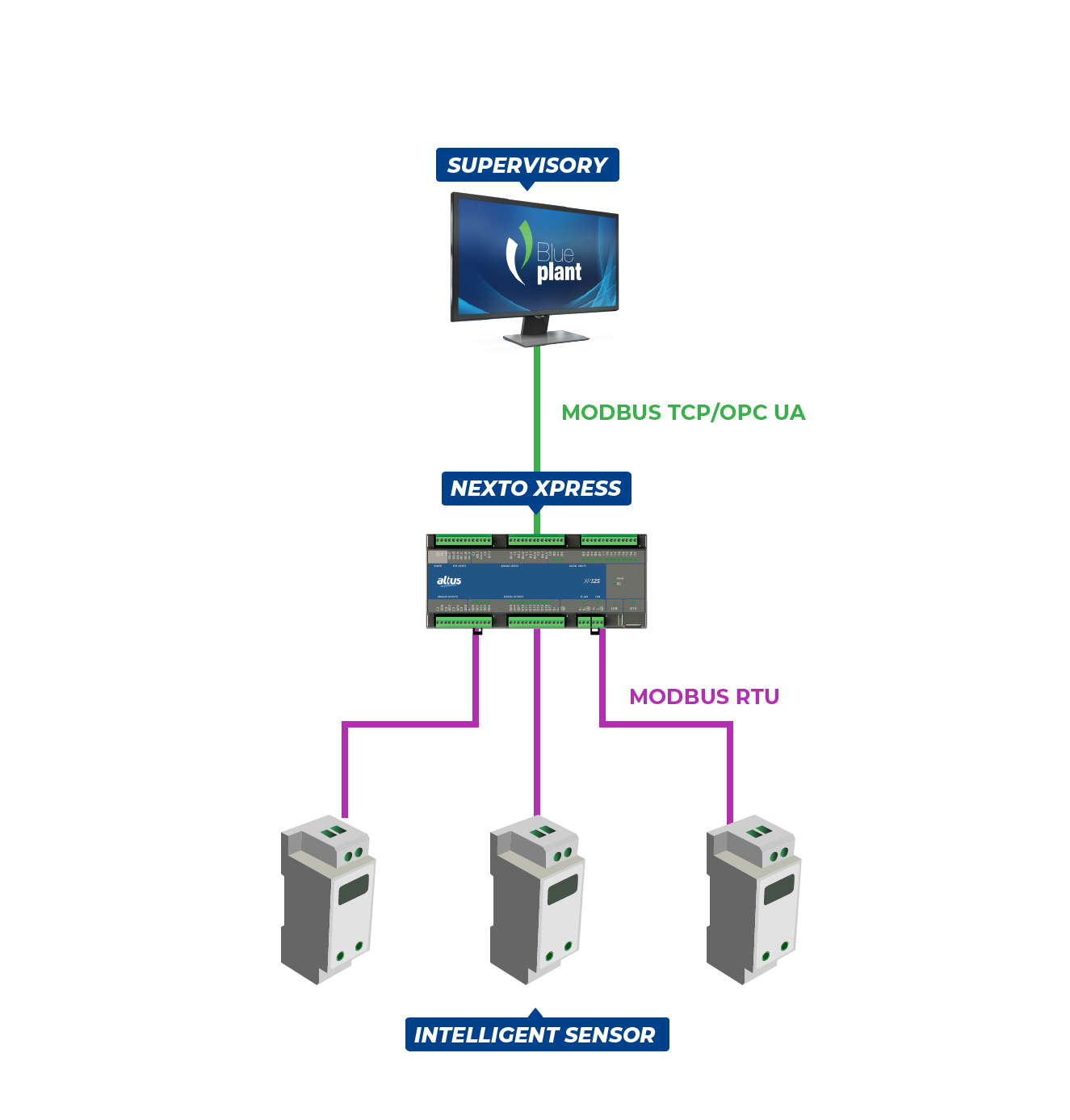
In addition, the Altus compact controller can also be used as a communication intermediary between smart sensors, actuators and the supervision system. As they have the capability to process the collected data, this type of field device can forward interpretable information directly to the supervisory resource. However, as these equipments usually only have serial type interfaces, with MODBUS RTU protocol, the Xpress PLC can perform the data conversion to MODBUS TCP or OPC UA standard and forward the information directly to the supervisory software.